Adverbs Used in Past Continuous Tense

The past continuous tense is used to describe actions that began in the past and often continued for a short period of time after the action started.
The past continuous (sometimes past progressive) tense is a really important tense used in English. This tense is very often used in daily conversation so it is really necessary to know how to use it.
The past continuous also combines the progressive aspect with the past tense using the past tense form of the irregular verb „to be" in combination with the verb in base form + the suffix –ing (present participle).
Look at past continuous tense examples.
When do we use the past continuous tense?
We use the past continuous tense to talk about many situations. For example, we use this tense to express:
Actions
We use the past continuous tense when we want to describe that something happened before/after some other action.
Example: Notice the difference between the two sentences
- Past continuous: Jamie and Polly were doing their homework when I came home.
- Past simple: Jamie and Polly did their homework when I got home.
In the first sentence we use the past continuous because we want to describe that Jamie and Polly were still doing their homework when I came home.
In the second sentence we use the past simple because the verb „did" means that Jamie and Polly had already finished their homework when I came home.
Lasting events
The past simple describes actions that lasted for some time, meaning we can use the tense to describe actions or feelings that continued for a period of time.
Example:
- I was feeling bad that day.
- They were shouting.
If we used the past simple 'I felt bad,' it would mean that I felt bad only in one moment. The past continuous describes that I was feeling bad for a longer period of time.
Repetitive actions
This tense is often used for describing repetitive events. When something was happening over and over again, we use the past continuous tense.
Example:
- She was playing the piano every Tuesday at 5 o'clock.
- They were having a meeting every week.
Specific time
The past continuous tense is also used to describe events that happened at a specific point in time.
Example:
- It was 5 o'clock. I was cleaning the bathroom.
This means I was cleaning the bathroom before and even after 5 o'clock. If we would use the past simple 'I cleaned the bathroom,' it would mean that I started to clean the bathroom.
Changing growth
We also use the past continuous tense to describe something that was changing. The change can be physical growth, mental growth or any other changes.
Example:
- Jamie was growing up really quickly.
- My Spanish was improving.
- My hair was going brown.
- Prague was changing really slowly.
Two actions at the same time
The past continuous tense also describes two events happening at the same time. This means we are using the past continuous in both events.
Example:
- While I was cooking, she was cleaning a bathroom.
- While she was looking for her keys, we were packing our luggage.
Interrupted action
This tense is often used to describe an action that was interrupted by some event. These kinds of sentences usually start with words such as „while" or „when" in the first or second part of the sentence.
In these kinds of sentences, the past continuous is combined with the past simple (past simple always illustrates that an event happened after another event).
Example:
- While I was playing basketball, he came in.
- We were watching the best video in the world when the video froze.
Adverbs that are used with the past continuous tense
You can also recognize the past continuous tense by using specific adverbs. The most common ones describe some repetitive actions as well as unplanned or undesired events. These adverbs are, for example, „forever", „always" or „constantly".
But be careful! When one of these words are used in a sentence, it doesn't automatically mean that it is the past continuous tense, so do not rely on that.
Example:
- We were always playing basketball together.
- She was constantly singing in the bathroom.
- He was forever losing his wallet.
Do not use stative verbs
We do not often use the past continuous tense in combination with stative verbs. Stative verbs are verbs which express a state rather than an action, and often relate to feelings like thoughts, emotions, relations or senses.
Instead of using the past continuous tense, we should use the past simple while still using the verb „was/were".
Example:
- I was tired.
- She was ill.
- They were lonely.
Construction of sentences
The verb „to be" is the most important verb in the past continuous tense. That's because if we want to describe anything in the past continuous tense, we need to use its past tense form, "was/were," in combination with the main verb and the – ing form.
To describe something specific, we can use the main verb „do", so the entire verb will be in the form „was/were doing." In this tense, we do not distinguish irregular verbs but instead always use the verb's base form with the suffix –ing.
The sentence would be as follows:
Subject + was/were + (verb + ing) + object
The verb „to be"
The verb „to be" is a special one in the past continuous tense. Because verbs „was/were" are the most important in the past continuous tense, we need to know how to use them.
There are specific rules on how to use the past tense form of verb „to be". In the past continuous tense, we use only its past tense form (2nd form), meaning we use only forms „was/were".
„Was" versus „were"
If we want to describe the verb „to be" in the past continuous tense, we need to use its irregular form. These two forms are WAS or WERE.
Was
We use „was" in sentences where the first or third person is singular, meaning we use it for subjects such as „I, He, She or It."
Example:
- I was doing my homework at 5 o'clock.
- She was looking for her keys for an hour.
- He was playing football yesterday.
Were
„Were" is used for subjects in other instances (You, We, They).
The verb „were" is also often used to replace the verb „was". It is very common in modern English to find sentences that use „were" instead of „was" in combination with the subject „I" even though it's grammatically correct to use „I was" instead.
„Were" is also very often used to describe conditional causes.
Example:
- They were playing basketball every weekend.
- We were reading a book for 3 hours on the train.
Affirmative sentences in the past continuous tense
The affirmative past continuous tense is composed of the 2nd form of the verb „to be" and the verb in its basic form with the suffix – ing.
While in the past simple we do not distinguish between a person or the number of subjects, in the past continuous tense it is different. We use the past tense form of the verb „to be", meaning we combine „was/were" with the base form verb + -ing.
This time it is easier in the sense that we do not have to memorize irregular forms of verbs like we had to for the past simple or past perfect tense. The only thing we need to know is how to use „was/were"and to know how to add the suffix – ing.
The complete sentence would be as follows:
Subject + was/were + (verb in base form + –ing) + object.
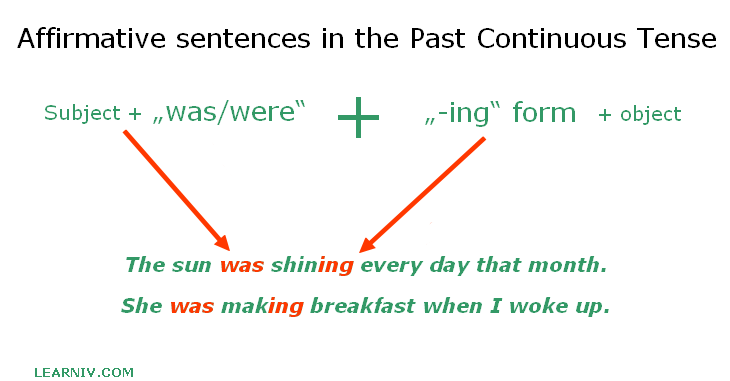
Examples:
- The sun was shining every day that month.
- She was making breakfast when I woke up.
- She was constantly talking in English classes these days.
Negative sentences in the past continuous tense
To describe the negative meaning of a sentence it is necessary to add negative (not) in front of „was/were". This means that to describe the negative meaning, we use „was not" or „were not". We can also use its shorter form „wasn't/weren't" in combination with the base form the verb + the suffix – ing.
If you want to use the negative meaning in a formal conversation, use „was not". This form is more formal than the shorter form and is therefore most suitable for the situation.
When we are talking to friends or family, we can use short forms. Short forms are often used in conversation with people you know and when it is not a formal situation.
The complete sentence would be as follows:
Subject + was/were not + (base form of verb + –ing) + object.

Example:
- My parents weren't cooking dinner this evening.
- I was not sleeping when you got home late last night.
- They were not listening to her.
Forming negative sentences is really easy in the past continuous tense. All we have to know is that we need to add the negative „not" after the verb „was" or „were".
Questions in the past continuous tense
To form a question in the past continuous tense, we have to put the verb „was/were" at the beginning of the sentence, in front of the subject. The rest of the sentence is similar to affirmative sentences. We are still using the verb in its base form in combination with the suffix –ing.
The complete sentence would be as follows:
Was / Were + subject + (verb in a base form + -ing) + object?
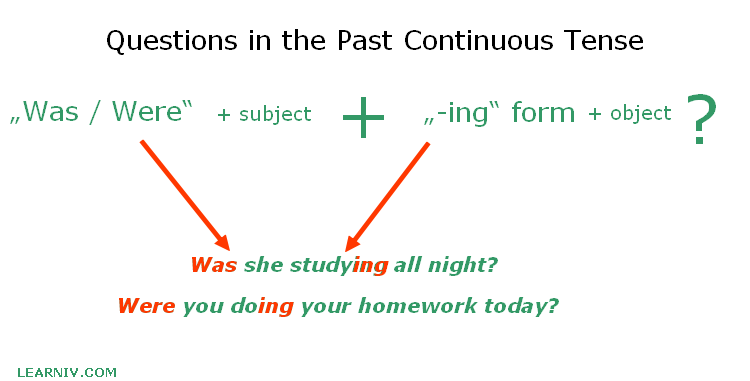
Example:
- Were you doing your homework today?
- Was she studying all night?
- Were we eating a lot of sandwiches today?
- Was I snoring tonight?
Past continuous + Past simple
We also very often use a combination of the past simple and past continuous tense. The past continuous tense is used for longer actions whereas the past simple is used for shorter ones that happened in the middle of the long action. In these kinds of sentences, we often use adverbs „when" or „while".
Example:
- Long actions – while (Past continuous)
- Short actions – when (Past simple)
- While I was playing the piano, you telephoned me.
- I was watching TV when someone knocked on the door.
Long action (playing the piano) is described by the past continuous and its termination (telephoned me) is denoted by the past simple.
The past continuous tense is a really easy tense to learn. The challenge lies in learning how to use it correctly instead of using an incorrect tense in its place.
Source: https://en.learniv.com/info/en/tenses/past-continuous-tense/
Post a Comment for "Adverbs Used in Past Continuous Tense"